Medical AI Research
1. Core Vision
의료 영상에서 단순 분류(Classification)가 아니라, 질병을 정량화(Quantification)하고, 구조화된 임상 표현(structured clinical representations)을 생성하여 LLM 기반의 임상 추론으로 연결되는 "End-to-End Clinical Reasoning Pipeline"을 구축하는 것이 전체적인 연구 비전입니다.
이 비전은 다음과 같은 핵심 목표를 가집니다:
- 의료 영상 → 병변 분할(segmentation) → 수치화(quantification) → 정량 지표 기반 예측 모델
- 정량 지표 + 이미지 + 텍스트 리포트 → Multimodal LLM 기반 AI Doctor Assistant
- 안전성·신뢰성 강화: 모델 검증(Formal Verification), 안전 뉴런 분석, mechanistic interpretability
2. Research Theme A: Medical Image Quantification & Disease Modeling
전통적인 CNN 기반 분류를 넘어, 질병의 진행 정도를 수치화하고 임상적으로 해석 가능한 continuous biomarker를 생성하는 연구 라인입니다.
A.1. Ophthalmology (안과 영상 기반 정량화)
- Epiretinal Membrane(ERM), Diabetic Retinopathy, Macular Disease 등
- Fundus / OCT-B-scans 기반:
- 병변 segmentation (Membrane, Retina layers, cyst regions)
- Thickness map, curvature, reflectance profile 등 정량 지표 생성
- 정량 지표 기반 disease staging, progression prediction 모델
A.2. Gait / Orthopedics (정형외과 보행 분석)
- Markerless video (pose estimation) → biomechanical features → gait anomaly quantification
- Clinical grading 대신 정량 feature를 활용한 진단 및 progression 모델
- Pediatric, elderly imbalance assessment 등 확장 가능
A.3. Multi-modal structured data integration
영상, 정량 feature, EMR, 검사 수치(labs) 등 통합.
최종 목적: disease progression world model 구축.
3. Research Theme B: Domain-Specialized Medical LLMs (Ophtimus-V2 계열)
사용자가 직접 개발한 Ophthalmology 특화 LLM(Ophtimus-V2-Tx) 연구 라인입니다.
B.1. Clinical reasoning 모델
- 케이스 리포트 기반 fine-tuning
- 증상–영상–진단–치료로 이어지는 "임상 지식 경로(clinical knowledge pathway)" 학습
- hallucination 감소 및 안전성 강화 목적의 LoRA 및 structured LoRA 실험
B.2. Multi-modal 입력 확장
- Fundus / OCT(B-scan) embedding + structured quantification + textual description
- 나아가 의료용 World Model과 결합하여 progression simulator 연동 가능
B.3. Safety & Trustworthiness
- "Safety Neurons" 분석
- Mechanistic interpretability (circuit-level patterns in reasoning)
- Clinically harmful output 검출 및 unlearning
4. Research Theme C: Formal Verification + AI Safety for Medical AI
의료 AI의 신뢰성과 규제 대응(의료기기 인허가 등)을 위해
정형 기법(Formal Methods) + AI Safety를 결합한 독자적 연구 라인.
C.1. Verified Environment Models
- Timed Automata 기반 의료 프로세스 모델
- Model checking(PCTL, CTL, TCTL)을 통한 안전 제약 조건 검증
- 강화학습 또는 AI inference가 이 제약을 위반하지 않도록 control shield 제공
C.2. Verified AI Controllers
- Medical AI inference pipeline에 safety property 강제
- "언제 어떤 입력에서 위험한 출력이 발생 가능한가"를 검증하는 분석
- Verification-aware fine-tuning 또는 pruning
C.3. Trustworthy Data & Contamination Check
- Crowd annotation에서 LLM-cheating 탐지(peer prediction 기반)
- 의료 데이터 라벨의 신뢰성 확보
5. Research Theme D: Medical World Models & Embodied AI
NeurIPS 2025의 핵심 트렌드("World Models", "Embodied AI for Healthcare")와 직접적으로 정렬되는 연구 방향.
D.1. Disease Progression World Model
- Retina / ERM progression dynamics를 모델링하는 generative world model
- OCT/B-scan 연속 영상 기반 temporal latent dynamics
- "만약 환자의 상태가 X라면, 6개월 후의 OCT는 어떻게 변할까?" 같은 counterfactual simulation 가능
D.2. Multi-modal Clinical Simulator
- 이미지, 정량 biomarker, 텍스트 리포트, 치료 이력 포함
- LLM에게 구조화된 임상 시뮬레이션 컨텍스트 제공
- 임상 결정지원(Decision Support) 최대 강화
D.3. Reinforcement Learning in Verified Clinical Simulation
- 실세계 의료를 직접 학습시키는 것이 금지되는 경우
- Verified world model 기반 safe RL 적용 가능
- Treatment planning 또는 screening 정책 최적화 연구로 확장 가능
6. Research Theme E: Foundations for AI-Driven Clinical Decision Support
위의 모든 축(A~D)를 통합하여 임상 추론 자동화라는 궁극적인 의료 AI 목적을 지원.
E.1. Image → Biomarker → Reasoner → Recommendation
- 완전히 end-to-end 연결 가능한 pipeline 구축
- 영상 기반 quantification이 LLM reasoning의 입력 구조로 연결됨
E.2. Multi-lingual / Multi-institution Generalization
- 한국, 미국(UPenn), 기타 기관 데이터 협력 기반
- Robustness, distribution shift 연구 수행
E.3. Regulatory-readiness
- 신뢰성 평가 지표(specificity, sensitivity, FN-critical tasks)
- "Safety case" 구조를 갖춘 의료 AI 문서화 가능
7. 전체 테마 요약 (One-page Executive Summary)
사용자의 Medical AI 연구는 단순한 이미지 분류를 넘어서 다음의 통합적 연구 생태계를 구축하는 것에 초점을 둔다.
- 질병 정량화 기술
- 영상 기반 병변 분석, 수치화, progression modeling
- 임상 특화 LLM 개발(Ophtimus-V2-Tx)
- Ophthalmology 전문 reasoning 모델
- Multi-modal (OCT/Fundus + EMR + biomarkers) 처리
- AI Safety & Formal Verification 적용
- 의료 AI를 위한 safety constraints 보장
- Verified environment + verified inference
- World Model 기반 임상 시뮬레이션
- 질병 진행 시뮬레이션
- LLM의 clinical decision reasoning을 위한 foundation
- 전반적 의료 의사결정 지원 시스템 구축
- Data → Image → Quantification → LLM → Decision까지 end-to-end
Key Themes
- Domain-specialized LLMs for ophthalmology (e.g., Ophtimus-V2-Tx)
- Noise-robust medical image analysis and quantification
- Reliable mapping from model outputs to clinical coding systems
- Evaluation frameworks for safety, robustness, and explainability
Selected Projects
- Ophtimus-V2-Tx: An 8B-parameter ophthalmology LLM trained on case reports and evaluated with CliBench-based coding.
- ERM Quantification: Low-cost and fast SD-OCT based epiretinal membrane detection and thickness quantification.
Ophtimus: Ophthalmology-specific LLM






🤗 Models and Datasets | 📕 AAAI 2025 workshop Paper
Introduction
Ophtimus is an open-source large language model (LLM) specialized in ophthalmology, built with 8 billion parameters based on the LLaMA architecture. It was trained on carefully curated ophthalmology-specific data, including medical papers, textbooks, and research reports. Through filtering, summarization, and preprocessing, only the most relevant and high-quality information was retained.
Designed to be both lightweight and high-performing, Ophtimus is suitable for real-world applications such as clinical decision support, medical education, and patient communication. The model and its training pipeline are fully open-sourced, providing a practical reference for developing similar domain-specific LLMs in other areas of medicine.
GitHub Repository: github.com/jinkimh/Ophtimus-Ophthalmology-LLM

Dataset Details
Note: All datasets were either newly constructed or adapted for this project. Pre-training datasets were curated from open-source ophthalmology materials, while instruction-tuning and evaluation datasets were built by extracting only ophthalmology-relevant samples from broader medical corpora. All data underwent preprocessing steps including deduplication, language filtering (English only), and removal of any personally identifiable information (PII).
| Dataset name | Source | Size | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ophthalmology-pubmed-corpus [Link] | Ophthalmology paper | 18.4M Tokens | Pre-Training |
• Map-reduce method summary • Broad ophthalmic keywords |
| Ophthalmology-textbook-corpus [Link] | Ophthalmology textbook | 4M Tokens | Pre-Training |
• Trusted medical sources • Rich in diagnostic cases |
| Ophthalmology MCQA Inst dataset [Link] | Ophthalmology Docs | 51.7k QAs | Inst-Tuning |
• Diverse multiple-choice formats • Reasoning included • Variety of ophthalmic topics |
| Ophthalmology EQA Inst dataset [Link] | Ophthalmology Docs | 49.3k QAs | Inst-Tuning | • Variety of ophthalmic topics |
| Ophtimus-Eval-Dataset [Link] | Medical platform data | 2,153 QAs | Evaluation |
• expert-verified data • MCQA dataset |
| PubMedQA-ophthal-Dataset [Link] | PubMedQA | 297 QAs | Evaluation |
• Ophthalmology domain filtered • True/False MCQA dataset |
| MedMCQA-Ophthal-Dataset [Link] | MedMCQA | 6,932 QAs | Evaluation |
• Ophthalmology domain filtered • MCQA dataset |
| EQAEval-Dataset [Link] | MedQuAD, Others | 1,389 QAs | Evaluation |
• Diverse open-source datasets • Ophthalmology domain filtered • Essay QA |
Model Details
Note: The "pre-training" and "fine-tuning" columns in the table refer to the training performed in this project. The base models had already undergone pre-training and/or fine-tuning prior to this project, and we applied transfer learning using those models.
| Model name | Base model | Parameters | Pre-training | Instruction-tuning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ophtimus-Base [Link] | Llama-3.1-8B | 8B | ✅ | ❌ |
| Ophtimus-Llama-1B [Link] | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 1B | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ophtimus-Llama-3B [Link] | Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 3B | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ophtimus-Llama-8B [Link] | Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | 8B | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ophtimus-Instruct-8B [Link] | Ophtimus-Base | 8B | ✅ | ✅ |
Performance
Note: Multi-Choice QA: Ophtimus-Eval, MedMCQA, PubMedQA | Essay QA: MedQuAD, Medical Flashcards, Medical Wikidoc
Ophtimus-Eval is a proprietary dataset collected from a medical platform. The others are established medical benchmark datasets, from which only ophthalmology-related QA pairs were extracted for evaluation.
| Model | Multi-Choice Question | Essay Question | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ophtimus Eval | MedMCQA (Ophth) | PubmedQA (Ophth) | RougeL | BLEU | METEOR | SemScore | |
| OpenAI GPT-4o | 71.95% | 81.95% | 89.90% | 0.193 | 0.082 | 0.341 | 0.761 |
| Llama-3-8B-Instrct | 48.60% | 74.02% | 63.97% | 0.193 | 0.064 | 0.244 | 0.684 |
| Llama-3.1-8B-Instrct | 39.78% | 57.96% | 83.84% | 0.177 | 0.054 | 0.215 | 0.641 |
| Eye-Llama | 32.56% | 59.43% | 66.11% | 0.183 | 0.062 | 0.211 | 0.686 |
| PMC-Llama-13B | 48.28% | 63.45% | 72.48% | 0.223 | 0.082 | 0.288 | 0.714 |
| Ophtimus-Llama-1B | 41.45% | 45.74% | 61.95% | 0.219 | 0.076 | 0.217 | 0.711 |
| Ophtimus-Llama-3B | 52.70% | 62.10% | 69.36% | 0.224 | 0.077 | 0.225 | 0.726 |
| Ophtimus-Llama-8B | 60.78% | 68.25% | 69.70% | 0.226 | 0.083 | 0.230 | 0.733 |
| Ophtimus-Instruct-8B | 63.85% | 71.51% | 72.73% | 0.222 | 0.079 | 0.224 | 0.735 |
Quickstart
Install Dependencies
cd Ophtimus-Ophthalmology-LLM
pip install -r requirements.txtOphtimus Inference
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
# model_name example : BaekSeungJu/Ophtimus-Instruct-8B or Ophtimus-Llama-1B or Ophtimus-Llama-3B or Ophtimus-Llama-8B
model_name = "BaekSeungJu/Ophtimus-Instruct-8B"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
trust_remote_code=True,
).to("cuda")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, padding_side="left")
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
system_instruction = (
"You are an expert ophthalmologist. Please provide accurate and "
"medically sound answers to the user's ophthalmology-related question."
)
# Enter your questions in the list
questions = [
"Please describe the symptoms and treatment of epiretinal membrane.",
"What's good for eyes?"
]
prompts = []
for question in questions:
row_json = [
{"role": "system", "content": system_instruction},
{"role": "user", "content": question}
]
prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(row_json, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
prompts.append(prompt)
input_ids = tokenizer(
prompts,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)["input_ids"].to("cuda")
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids,
max_new_tokens=1024,
do_sample=False,
)
decoded = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=False)
for i, text in enumerate(decoded):
print(f"------------------------\nAnswer for question {i+1}:\n{text}")For more details, visit the GitHub repository.
Ophtimus-V2-TX
To be Updated
SD-OCT-based Epiretinal Membrane Diagnostic Assistant System





Introduction
This project presents a low-cost and efficient method for detecting and quantifying Epiretinal Membranes (ERM) using Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (SD-OCT). By applying deep learning techniques—specifically, YOLO object detection—we generate en face "ERM Projection Images" from B-scan data, enabling intuitive visualization and accurate measurement of ERM areas. The method also introduces a novel approach to quantify the association between ERM and retinal thickness, enhancing clinical decision-making. Our approach aims to bridge the diagnostic performance gap between SD-OCT and Swept-Source OCT (SS-OCT) while maintaining accessibility and reducing diagnostic burden.
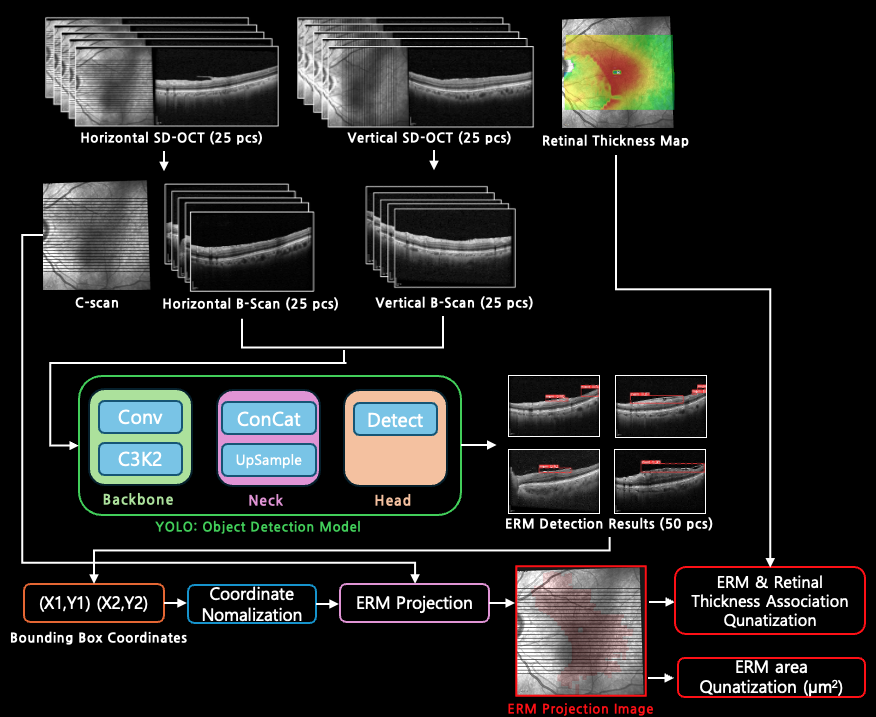
Overall pipeline architecture for ERM detection & quantification
YOLO Model Evaluation
We evaluated three YOLO-based models (v5, v8, v11) for ERM detection using SD-OCT B-scan images.
Each model was trained on two datasets (2,200 images for Full, 1,100 images for Half) and tested on 650 expert-labeled images.
| Model | Size | Params (M) | Precision | Recall | mAP@50 | mAP@50:95 | Dataset Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | S | 7.02 | 0.752 | 0.703 | 0.722 | 0.423 | Full |
| 0.694 | 0.642 | 0.664 | 0.376 | Half | |||
| M | 20.87 | 0.783 | 0.734 | 0.752 | 0.444 | Full | |
| 0.723 | 0.685 | 0.701 | 0.396 | Half | |||
| L | 46.14 | 0.813 | 0.762 | 0.784 | 0.463 | Full | |
| 0.745 | 0.704 | 0.726 | 0.414 | Half | |||
| X | 86.22 | 0.836 | 0.784 | 0.802 | 0.485 | Full | |
| 0.763 | 0.725 | 0.743 | 0.437 | Half | |||
| YOLOv8 | S | 11.14 | 0.781 | 0.736 | 0.764 | 0.447 | Full |
| 0.723 | 0.676 | 0.701 | 0.393 | Half | |||
| M | 25.86 | 0.813 | 0.762 | 0.791 | 0.466 | Full | |
| 0.748 | 0.705 | 0.724 | 0.412 | Half | |||
| L | 43.63 | 0.844 | 0.792 | 0.823 | 0.482 | Full | |
| 0.774 | 0.731 | 0.754 | 0.436 | Half | |||
| X | 68.15 | 0.867 | 0.814 | 0.842 | 0.504 | Full | |
| 0.793 | 0.752 | 0.772 | 0.454 | Half | |||
| YOLOv11 | S | 9.43 | 0.804 | 0.752 | 0.783 | 0.468 | Full |
| 0.746 | 0.692 | 0.714 | 0.417 | Half | |||
| M | 20.05 | 0.846 | 0.794 | 0.821 | 0.493 | Full | |
| 0.774 | 0.736 | 0.757 | 0.443 | Half | |||
| L | 25.31 | 0.873 | 0.823 | 0.854 | 0.524 | Full | |
| 0.807 | 0.773 | 0.793 | 0.476 | Half | |||
| X | 56.87 | 0.902 | 0.857 | 0.882 | 0.556 | Full | |
| 0.836 | 0.803 | 0.826 | 0.507 | Half |
GitHub repository: github.com/jinkimh/SD-OCT-ERM-Quantification
Gait Anomaly Detection
To be Updated
