Medical AI Projects
This page summarizes ongoing and past projects in medical AI, with a particular focus on ophthalmology, retinal imaging, and trustworthy clinical decision support.
Key Themes
- Domain-specialized LLMs for ophthalmology (e.g., Ophtimus-V2-Tx)
- Noise-robust medical image analysis and quantification
- Reliable mapping from model outputs to clinical coding systems
- Evaluation frameworks for safety, robustness, and explainability
Selected Projects
- Ophtimus-V2-Tx: An 8B-parameter ophthalmology LLM trained on case reports and evaluated with CliBench-based coding.
- ERM Quantification: Low-cost and fast SD-OCT based epiretinal membrane detection and thickness quantification.
- Trustworthy Clinical Support: Methods to validate and monitor LLM predictions before deployment in real clinical workflows.
Ophtimus: Ophthalmology-specific LLM
Python · PyTorch · Transformers · LangChain · Streamlit · FastAPI

🤗 Models and Datasets | 📕 AAAI 2025 Workshop Paper
Introduction
Ophtimus is an open-source large language model (LLM) specialized in ophthalmology, built with 8 billion parameters based on the LLaMA architecture. It is trained on carefully curated ophthalmology-specific data, including medical papers, textbooks, and research reports. Through filtering, summarization, and preprocessing, only the most relevant and high-quality information was retained.
Designed to be both lightweight and high-performing, Ophtimus is suitable for real-world applications such as clinical decision support, medical education, and patient communication. The model and its training pipeline are fully open-sourced, providing a practical reference for developing similar domain-specific LLMs in other areas of medicine.
Related GitHub Repositories
•
Ophtimus-Ophthalmology-LLM
•
SD-OCT-ERM-Quantification
Dataset Details
All datasets used for Ophtimus were either newly constructed or adapted for this project. Pre-training datasets were curated from open-source ophthalmology materials, while instruction-tuning and evaluation datasets were obtained by extracting only ophthalmology-relevant samples from broader medical corpora. All data underwent preprocessing steps, including deduplication, English-only filtering, and removal of any personally identifiable information (PII).
| Dataset name | Source | Size | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ophthalmology-pubmed-corpus | Ophthalmology papers | 18.4M Tokens | Pre-Training |
• Map-reduce style summaries • Broad ophthalmic keywords |
| Ophthalmology-textbook-corpus | Ophthalmology textbooks | 4M Tokens | Pre-Training |
• Trusted medical sources • Rich in diagnostic cases |
| Ophthalmology MCQA Inst Dataset | Ophthalmology documents | 51.7k QAs | Instruction-Tuning |
• Diverse multiple-choice formats • Reasoning included • Various ophthalmic topics |
| Ophthalmology EQA Inst Dataset | Ophthalmology documents | 49.3k QAs | Instruction-Tuning |
• Essay / explanation-style QA • Variety of ophthalmic topics |
| Ophtimus-Eval-Dataset | Medical platform data | 2,153 QAs | Evaluation |
• Expert-verified data • Multi-choice QA dataset |
| PubMedQA-ophthal-Dataset | PubMedQA | 297 QAs | Evaluation |
• Ophthalmology domain filtered • True/False MCQA dataset |
| MedMCQA-Ophthal-Dataset | MedMCQA | 6,932 QAs | Evaluation |
• Ophthalmology domain filtered • Multi-choice QA dataset |
| EQAEval-Dataset | MedQuAD, others | 1,389 QAs | Evaluation |
• Diverse open-source datasets • Ophthalmology domain filtered • Essay-style QA |
Model Details
The pre-training and instruction-tuning columns below refer to the training conducted in this project. The base models had already undergone their own pre-training and/or fine-tuning, and Ophtimus was built using transfer learning on top of these models.
| Model name | Base model | Parameters | Pre-training | Instruction-tuning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ophtimus-Base | Llama-3.1-8B | 8B | ✅ | ❌ |
| Ophtimus-Llama-1B | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct | 1B | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ophtimus-Llama-3B | Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct | 3B | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ophtimus-Llama-8B | Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | 8B | ❌ | ✅ |
| Ophtimus-Instruct-8B | Ophtimus-Base | 8B | ✅ | ✅ |
Performance
Multi-Choice QA: Ophtimus-Eval, MedMCQA, PubMedQA (ophthalmology-subset)
Essay QA: MedQuAD, Medical Flashcards, Medical Wikidoc (ophthalmology-filtered)
Ophtimus-Eval is a proprietary dataset collected from a medical platform. The other datasets are established medical benchmarks, from which only ophthalmology-related QA pairs were extracted for evaluation.
| Model | Multi-Choice Question | Essay Question | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ophtimus Eval | MedMCQA (Ophth) | PubMedQA (Ophth) | RougeL | BLEU | METEOR | SemScore | |
| OpenAI GPT-4o | 71.95% | 81.95% | 89.90% | 0.193 | 0.082 | 0.341 | 0.761 |
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 48.60% | 74.02% | 63.97% | 0.193 | 0.064 | 0.244 | 0.684 |
| Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | 39.78% | 57.96% | 83.84% | 0.177 | 0.054 | 0.215 | 0.641 |
| Eye-Llama | 32.56% | 59.43% | 66.11% | 0.183 | 0.062 | 0.211 | 0.686 |
| PMC-Llama-13B | 48.28% | 63.45% | 72.48% | 0.223 | 0.082 | 0.288 | 0.714 |
| Ophtimus-Llama-1B | 41.45% | 45.74% | 61.95% | 0.219 | 0.076 | 0.217 | 0.711 |
| Ophtimus-Llama-3B | 52.70% | 62.10% | 69.36% | 0.224 | 0.077 | 0.225 | 0.726 |
| Ophtimus-Llama-8B | 60.78% | 68.25% | 69.70% | 0.226 | 0.083 | 0.230 | 0.733 |
| Ophtimus-Instruct-8B | 63.85% | 71.51% | 72.73% | 0.222 | 0.079 | 0.224 | 0.735 |
SD-OCT-based Epiretinal Membrane Diagnostic Assistant System
Python · PyTorch · OpenCV · YOLO · Pillow
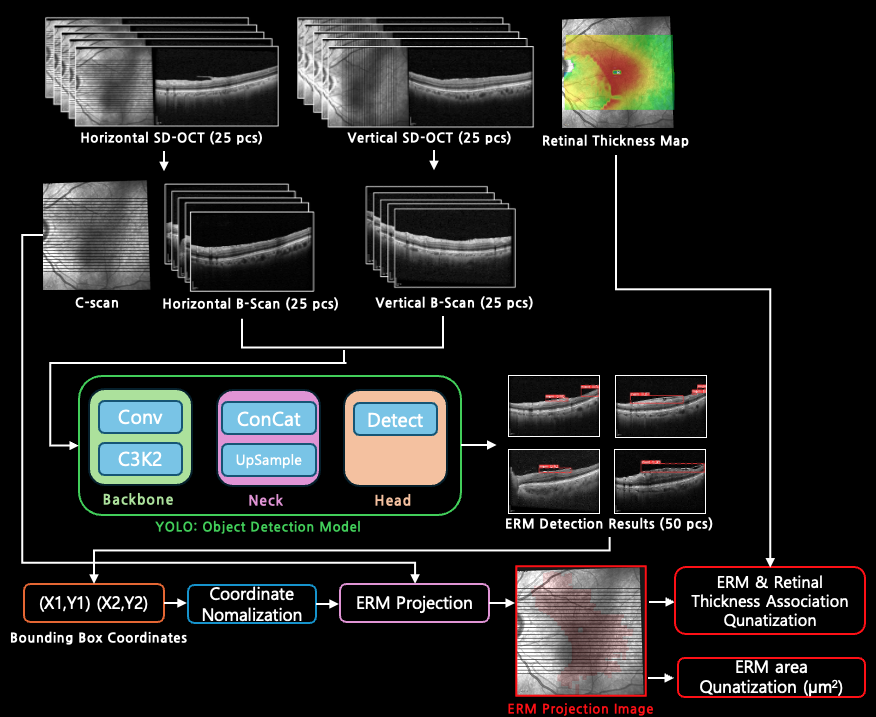
Overall pipeline architecture for ERM detection & quantification
Introduction
This project presents a low-cost and efficient method for detecting and quantifying Epiretinal Membranes (ERM) using Spectral-Domain OCT (SD-OCT). Using deep learning techniques—particularly YOLO object detection—we generate en face ERM Projection Images from B-scan data, enabling intuitive visualization and accurate measurement of ERM lesions.
The proposed approach also quantifies the association between ERM severity and retinal thickness, contributing toward enhanced clinical decision-making. This system aims to reduce the diagnostic gap between SD-OCT and Swept-Source OCT (SS-OCT) while maintaining accessibility and diagnostic performance.
GitHub repository: github.com/jinkimh/SD-OCT-ERM-Quantification
YOLO Model Evaluation
We evaluated YOLOv5, YOLOv8, and YOLOv11 models for ERM detection. Each model was trained with two dataset scales (Full: 2200 images, Half: 1100 images) and tested on 650 expert-labeled OCT B-scans.
| Model | Size | Params (M) | Precision | Recall | mAP@50 | mAP@50:95 | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | S | 7.02 | 0.752 | 0.703 | 0.722 | 0.423 | Full |
| YOLOv5 | S | 7.02 | 0.694 | 0.642 | 0.664 | 0.376 | Half |
| YOLOv5 | M | 20.87 | 0.783 | 0.734 | 0.752 | 0.444 | Full |
| YOLOv5 | M | 20.87 | 0.723 | 0.685 | 0.701 | 0.396 | Half |
| YOLOv5 | L | 46.14 | 0.813 | 0.762 | 0.784 | 0.463 | Full |
| YOLOv5 | L | 46.14 | 0.745 | 0.704 | 0.726 | 0.414 | Half |
| YOLOv5 | X | 86.22 | 0.836 | 0.784 | 0.802 | 0.485 | Full |
| YOLOv5 | X | 86.22 | 0.763 | 0.725 | 0.743 | 0.437 | Half |
| YOLOv8 | S | 11.14 | 0.781 | 0.736 | 0.764 | 0.447 | Full |
| YOLOv8 | S | 11.14 | 0.723 | 0.676 | 0.701 | 0.393 | Half |
| YOLOv8 | M | 25.86 | 0.813 | 0.762 | 0.791 | 0.466 | Full |
| YOLOv8 | M | 25.86 | 0.748 | 0.705 | 0.724 | 0.412 | Half |
| YOLOv8 | L | 43.63 | 0.844 | 0.792 | 0.823 | 0.482 | Full |
| YOLOv8 | L | 43.63 | 0.774 | 0.731 | 0.754 | 0.436 | Half |
| YOLOv8 | X | 68.15 | 0.867 | 0.814 | 0.842 | 0.504 | Full |
| YOLOv8 | X | 68.15 | 0.793 | 0.752 | 0.772 | 0.454 | Half |
| YOLOv11 | S | 9.43 | 0.804 | 0.752 | 0.783 | 0.468 | Full |
| YOLOv11 | S | 9.43 | 0.746 | 0.692 | 0.714 | 0.417 | Half |
| YOLOv11 | M | 20.05 | 0.846 | 0.794 | 0.821 | 0.493 | Full |
| YOLOv11 | M | 20.05 | 0.774 | 0.736 | 0.757 | 0.443 | Half |
| YOLOv11 | L | 25.31 | 0.873 | 0.823 | 0.854 | 0.524 | Full |
| YOLOv11 | L | 25.31 | 0.807 | 0.773 | 0.793 | 0.476 | Half |
| YOLOv11 | X | 56.87 | 0.902 | 0.857 | 0.882 | 0.556 | Full |
| YOLOv11 | X | 56.87 | 0.836 | 0.803 | 0.826 | 0.507 | Half |